18 min to read
How to Master Test Automation: A Step-By-Step Guide to Test Automation for Beginners
 Introduction
Introduction
Did you know that the global market for software testing is slated to reach $109.5 billion by 2027? According to a Global Software Testing Industry report, this industry was valued at $51.8 billion in 2023 and is witnessing a steady compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7% year over year. These numbers are evidence of the drastic advances in the testing industry and how it has evolved to accelerate the time to market for software, ensuring the highest test quality.
As testing teams worldwide concentrate on enhancing process efficiency, improving accuracy, and reducing time to market, test automation adoption takes center stage. Simply put, test automation is a methodology that deploys software tools to automate the execution of test cases instead of manual testing, which is time-consuming and prone to errors. While contributing to significant improvements in the speed and efficiency of the testing process, this testing technique also boosts output accuracy and reliability.
Testing teams follow a predefined sequence of steps to ensure the success of the automation testing process. This overview is termed an automation testing life cycle (ATLC), which details all the necessary actions and cautions that testers must consider before beginning the test.
 The automation testing life cycle
The automation testing life cycle
The automation testing life cycle empowers the testing team to determine the essential elements of projects well in advance. It helps them avoid mistakes at the early stages while carrying out the automation procedure. The automation testing life cycle expands over six major phases, namely:
- Determination of the scope of test automation
- Selection of the most suitable automation tool
- Test automation plan, design, and strategy
- Setting up the test environment
- Test script development and execution
- Test result generation, analysis, and reporting
Implementing these six stages of the test automation lifecycle ensures successful testing and delivers the most favorable outcomes. Now that we understand the testing lifecycle, let’s explore the various types of automation testing.
 Test automation types
Test automation types
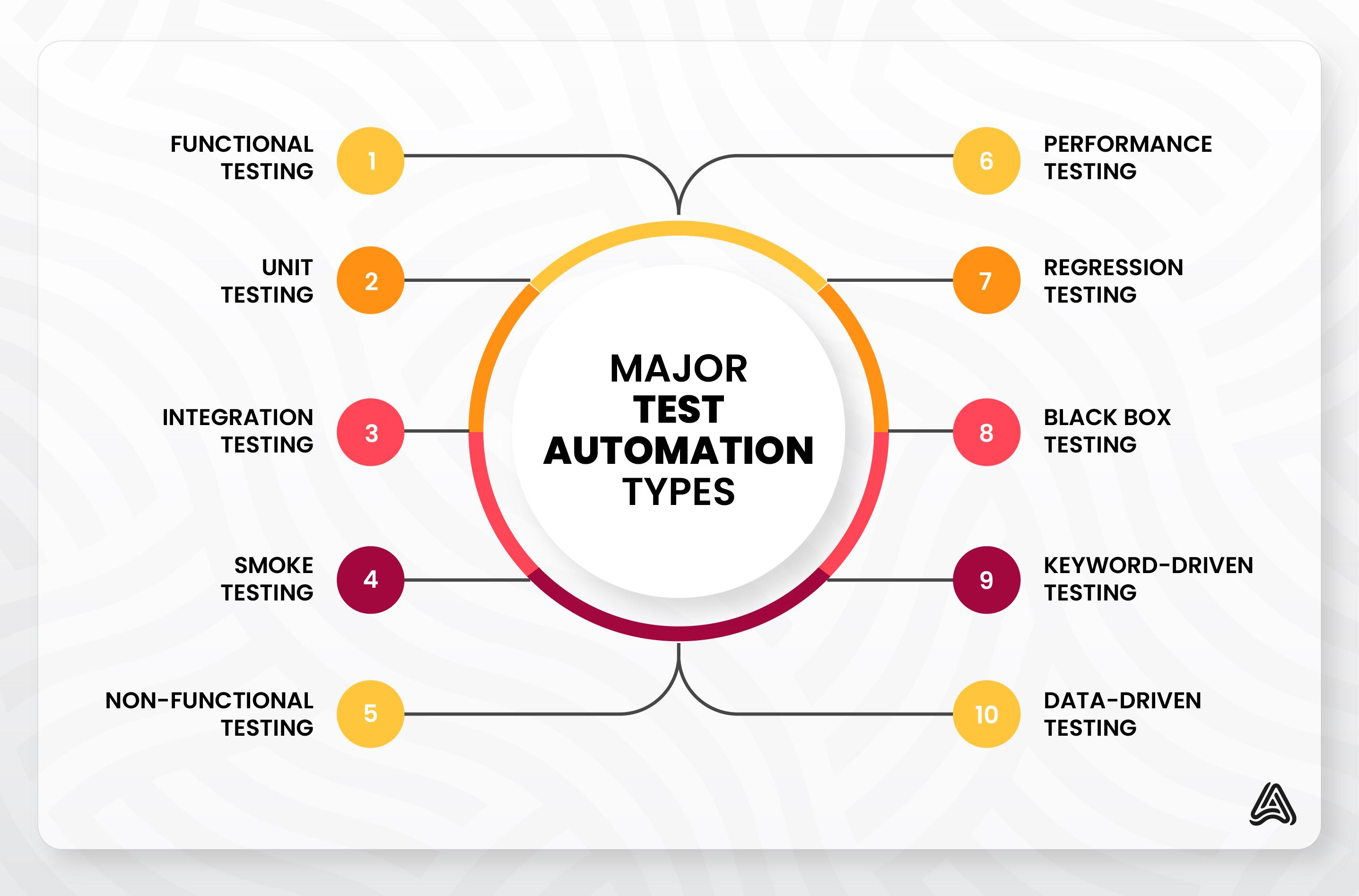
Knowing the types of testing methods available is a good practice before implementing test automation suites for your quality assurance (QA) team. It gives you a sound understanding of an automation program’s extensiveness before integrating it into your QA environment. It also lets you decide on the testing type to deliver the most favorable results.
The following table showcases the most common types of automation testing methods and their primary features.
| Test Type | Description | Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Functional Testing | It evaluates software against predefined functional requirements or specifications using primarily black-box testing (behavioral testing), where the tester is unaware of the internal design or structure of the test item. | Focuses on the system’s fundamental tasks, usability, and accessibility Examples: Integration testing, User acceptance testing, Smoke testing, Unit testing |
| Unit Testing | Performed by developers to test individual elements or functions in isolation, verifying that they work as intended. It helps identify bugs early in development, reducing the cost of bug fixes and facilitating code reusability. | Precedes integration testing. Categories: Black-box, White-box, and Grey-box testing |
| Integration Testing | It examines the combined interaction between different modules and evaluates whether the system meets its functional requirements. It typically follows unit testing to ensure optimal software functioning. | Approaches: Top-down, Bottom-up, Sandwich, Big Bang |
| Smoke Testing | It comprises a minimal set of tests to examine the stability and viability of the deployed software build, ensuring that vital application blocks are functional before proceeding to further testing phases. | Also known as Build verification or Confidence testing. Determines if the application should continue testing or return to development for modification |
| Non-functional Testing | It focuses on testing non-functional aspects of an application, such as performance, usability, and reliability, emphasizing how well the product performs rather than what it does. | Logical sequence: Follows functional testing. Includes scalability, performance, security, reliability, load, compatibility testing |
| Performance Testing | It tests software’s speed, stability, and responsiveness under stress to identify and eliminate bottlenecks and optimize its ability to deliver peak performance. | Critical for software that requires high reliability. Examples: Testing of critical software and medical programs |
| Regression Testing | It involves rerunning functional and non-functional tests after program changes to ensure that existing functionalities remain unaffected and the software’s performance is consistent. | Ensures no regression in functionality after code revisions |
| Keyword-driven Testing | It utilizes data files containing keywords associated with specific actions within the application. This method automatically triggers actions linked to recognized keywords, offering flexibility and ease of maintenance. | Widely used for its flexibility and maintainability |
| Data-driven Testing | Employs external data (stored separately in spreadsheets or tables) fed into test cases, allowing the same test to be applied across multiple data sets, thus saving time and resources and promoting code reusability. | Efficient for testing with multiple data sets. Enhances consistency and reusability |
| Black-box Testing | The tester isn’t familiar with the software’s implementation details but focuses on examining the functionality based on a specification or requirement list. | Test cases are reproducible and efficient for implementing tests in the more extensive system. Functional knowledge or programming skills aren’t requisite |
Table 1: A tabular representation comparing the prominent test types
Quantifying the merits and limitations of various automation types can help you ideate your test automation strategy more effectively. The key is to employ a coordinating combination of these testing types to reap the benefits of automation.
 Standout benefits of test automation techniques
Standout benefits of test automation techniques
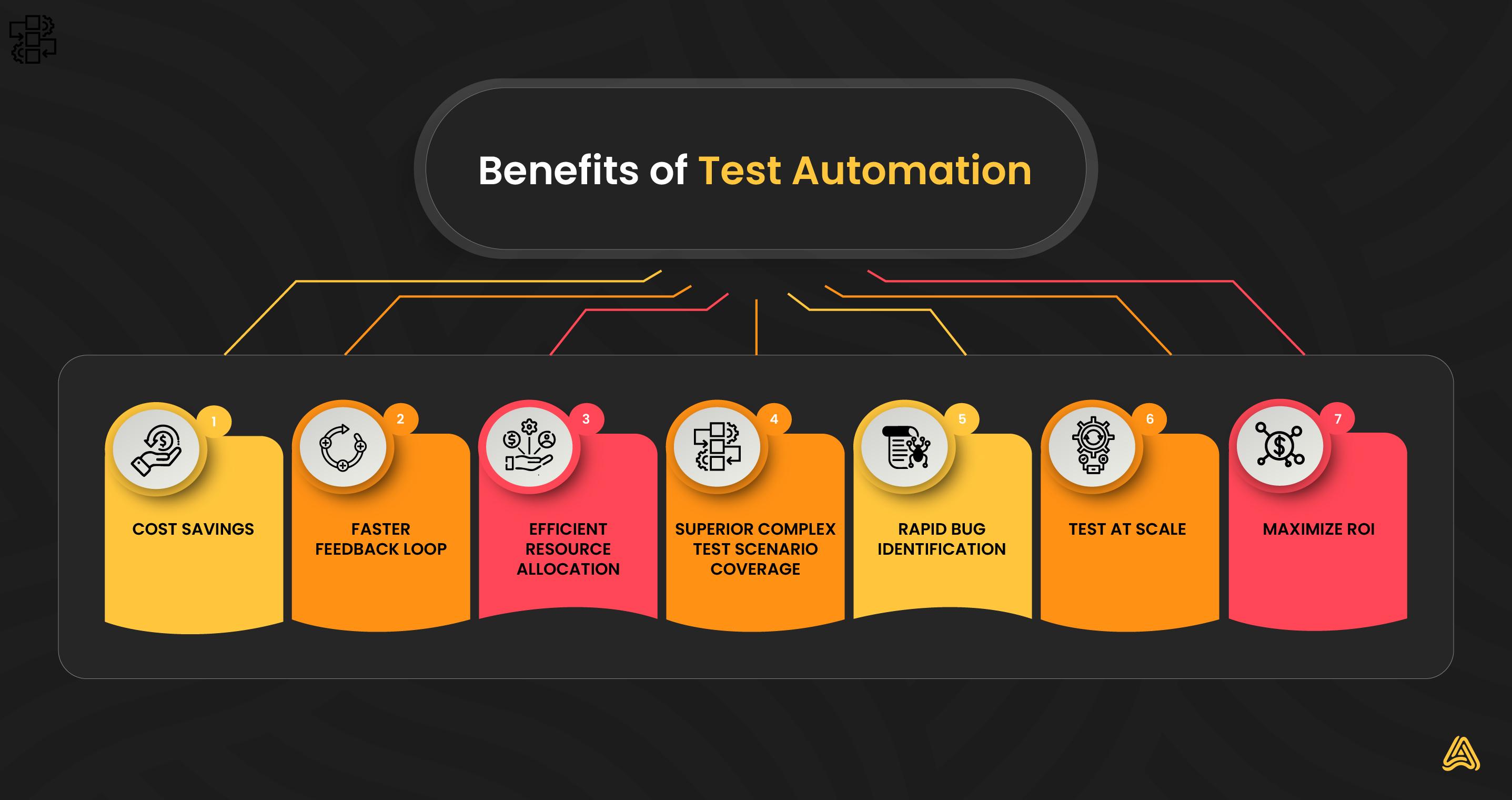
The advantages of test automation are not limited to higher speed and better efficiency in testing procedures. This technology also offers various other benefits to the software development teams, such as:
 Cost savings in the long run
Cost savings in the long run
Higher initial costs are a significant factor preventing organizations from adopting test automation. Additional staffing requirements, time constraints, and maintenance overheads are prerequisites for a successful automation test suite, and these prerequisites may prevent organizational management from adopting this testing technique.
However, the capital spent upfront is eventually recoverable by the cost savings that leaner and more effective software development offers. Upon completion of the setup, a team can use it repetitively at a fraction of the cost of a group of human testers. Organizations can save money by fixing errors faster and early in the software development life cycle.
 Faster feedback loop
Faster feedback loop
Test automation via all modern-day frameworks drastically accelerates test case execution. They help machines work faster, specifically for repetitive tasks such as regression testing and integration. QA teams can obtain feedback sooner, which aids in faster bug detection and better functionality.
Faster feedback loops offer an agility boost to test automation life cycles and help developers seamlessly integrate push code, receive feedback, and revise the code. Automation allows tests to execute faster to get accurate outputs in shorter sprints while facilitating flawless feedback.
 Efficient resource allocation
Efficient resource allocation
With automation dealing with repetitive processes, QA personnel can shift their attention to activities that require judgment and cognitive engagement. Examples of these activities could be formulating new test cases, determining advanced testing metrics, examining test results minutely, etc. Test automation reduces the monotony of testing tasks and enables testers to be more productive in day-to-day roles.
 Enhanced complex test scenario coverage
Enhanced complex test scenario coverage
Embracing the power of automation helps QAs execute a larger number of test cases to ascertain the maximum coverage of features and requirements in every test cycle. A broader test coverage raises the possibility of detecting bugs that fend off avoidable issues to go into production.
 Rapid bug detection
Rapid bug detection
With the advantage of test automation, developers can run unit tests before pushing code to version control and follow up with other test types. As every line of code gets tested extensively, earlier bug detection becomes possible. Faster and earlier bug detection opens the door for rapid and easier debugging.
 Test at scale
Test at scale
Regardless of the size and efficiency of your QA team, it simply can’t match the accuracy, speed, and range of an automation framework. For context, automation can help you simulate the activity of a thousand users on a site for load testing. Unless a QA team consists of more than a thousand members who are willing to browse a website simultaneously, manual testing can’t achieve it. Test automation supports parallel testing, which enables you to execute multiple tests simultaneously, helping you test at scale and speed.
 Maximize RoI
Maximize RoI
Test automation lets you accelerate product release without compromising the software build quality. It helps you achieve lower time-to-market and boosts your business’s Return on Investment(RoI).
The merits of test automation bring many benefits for enterprises that consistently look to build and deliver fresh products. Faster testing cycles, better accuracy, lower costs, and enhanced teamwork give QA teams a competitive advantage. Let’s look at the best practices to help you leverage the true scope of test automation for your organization.
 Best practices in test automation
Best practices in test automation
Test automation helps ensure optimal software operation and performance while offering an error-free user experience across platforms and devices. It also imparts extended coverage and precise outcomes that improve long-term product quality. However, to make test automation successful, you must familiarize yourself with the right tools, technical expertise, and test automation frameworks. Following a set of best practices can help you better execute automated tests while managing your resources effectively. Let’s explore the best practices in test automation that you must plan to implement.
 Decide the test cases to automate
Decide the test cases to automate
Determine the test cases that should be automated first, as it’s pretty impractical and unnecessary to automate all the cases. Devise a test automation plan by deciding which tests will excel from being automated. To ensure the best results, automate:
- Repetitive tests that run for several builds
- Tests that are prone to human error
- Tests that require multiple data sets
- Test that are impossible to execute manually
- Test that runs on various configurations, software platforms, and hardware
 Divide tasks based on skillset
Divide tasks based on skillset
Assign each case to particular individuals based on technical prowess while creating test suites and cases. This allocation will enable team members with different skill levels to draft test scripts with considerably minimal ease. A few complications may arise if the team chooses to use open-source tools, as designing the tests requires someone capable of coding with that specific tool.
 Establish collective ownership of tests
Establish collective ownership of tests
Delegating a sole tester or engineer to carry out full-fledged automation testing projects defeats the purpose of qualitative testing. Ensure the entire team is looped in to enable meaningful contributions to better integrate automation into the testing infrastructure. This will help members familiarize themselves with the process and make timely decisions about conducting suitable tests.
 Eliminate scopes of uncertainty
Eliminate scopes of uncertainty
Every additional false positive and inconsistency increases the time needed to scrutinize errors. To avoid this loss of time, you must remove uncertainties by extracting unstable tests in regression packs. Plan your testing adequately to ensure you don’t miss out on inspecting vital verifications, as they are common occurrences in automation tests. Additionally, ensure that the validity of test automation is thoroughly assessed throughout the test cycles.
 Select the right test tool or framework
Select the right test tool or framework
A suitable test automation tool can make your testing experience effortless. Consider the following points to choose the tool that best suits your needs.
- Check if the testing tool extends support for your platforms and technology.
- Confirm if the tool provides a higher level of flexibility for testers of varying skill levels.
- Verify if the test tool can seamlessly integrate with your enterprise’s existing ecosystem.
 Test on actual devices
Test on actual devices
Ensure to conduct your tests on real devices or browsers, as the product needs to work appropriately on cross-platform multiple device-browser-OS combinations. A simulator or emulator can’t replicate real user interactions. Testing on actual devices helps evaluate if the product can work in real-world scenarios such as weak network strength, incoming calls, lower battery, etc.
 Maintain records for better debugging
Maintain records for better debugging
Keeping records of failure scenarios in text or video log formats can help testers determine the reasons behind test failures. Selecting a tool with built-in support for automatically recording browser screenshots for each step is ideal for easily detecting errors in every step.
 Employ data-driven tests
Employ data-driven tests
The massive volume of data and the number of variables make it ambiguous for humans to conduct fast and accurate tests. Utilizing data-driven automation tests reduces the task to a single test and data set, which testers can use to work through an array of parameters and simplify the process.
 Conduct tests frequently
Conduct tests frequently
Frequently running tests can help testers identify bugs as they appear and debug them immediately. It helps save time and valuable resources that could skyrocket if bug detection happens at later development and production stages.
 Prioritize quality test reporting
Prioritize quality test reporting
Set up a robust test reporting infrastructure with the appropriate tools to generate elaborate, high-quality reports for every test. A good practice is to group tests according to parameters such as results, type, tag functionality, etc.
The right tools can help you maximize the advantages of test automation in terms of coverage, efficiency, and accuracy while supporting continuous integration for repetitive tasks. These tools allow you to extract the best out of your test automation procedures while adhering to all the best practices in automation.
 Popular test automation tools
Popular test automation tools
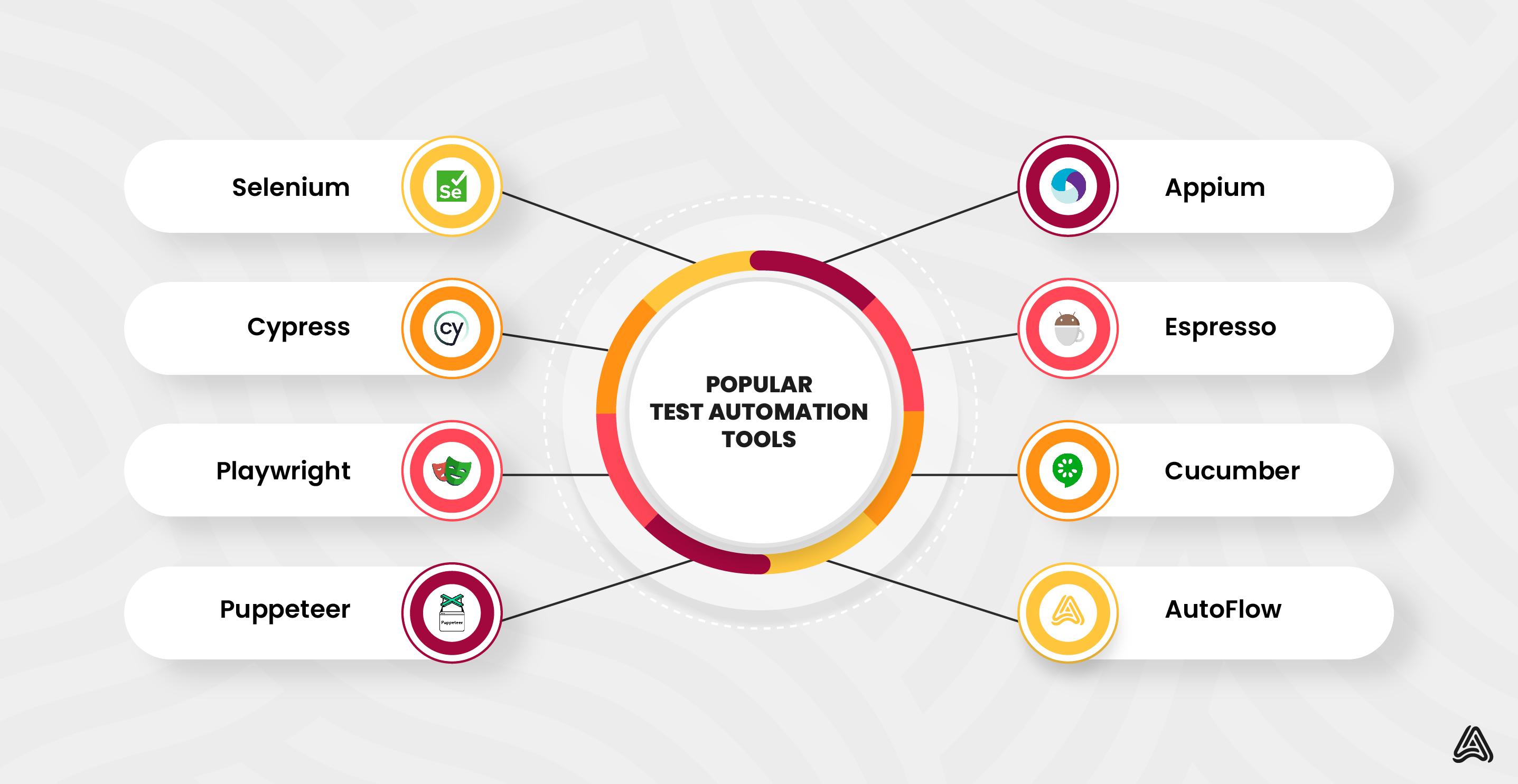
Test automation tools help maintain consistency across varied testing environments. They empower QA teams to prioritize features over repetitive tasks. A few of the standout tools and their use cases are as follows.
| Tool | Description | Key Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Selenium | It is a popular open-source test automation framework for web applications. Selenium simulates user interactions and automatically validates web application behavior. Selenium supports multiple languages, including Python, C#, Java, and JavaScript. | Testing browser extensions, Online task automation, Interactive demos, Data extraction |
| Cypress | It is a modern JavaScript-based end-to-end test automation framework known for its speed, efficiency, and intuitive API. Cypress simplifies test scripting and maintenance, reduces flakiness, and boosts test stability through automatic waiting. | Real-time collaboration testing, Network traffic control, Advanced debugging capabilities, Accessibility testing |
| Playwright | Developed by Microsoft, Playwright supports web, mobile, and desktop application test automation. It offers versatility, rich API setup, and native support for handling uploads, downloads, and browser context management. | Testing Progressive Web Applications (PWAs), Multi-platform application testing |
| Puppeteer | A Google-created Node.js library, Puppeteer is ideal for controlling headless Chrome or Chromium browsers. It provides a high-level API for automating UI testing, form submission, keyboard input, and more without a graphical interface. | Automated form filling, PDF generation, Headless browser tasks, Performance monitoring |
| Appium | It is an open-source test automation tool specifically for mobile applications. Appium uses the mobile JSON wire protocol to script automated UI tests for native, web-based, and hybrid apps on Android and iOS platforms. | Client mobile app testing, Outsourced regression testing, Cross-device compatibility testing, UI/UX verification services |
| Espresso | A Google automation framework that allows QA teams to create and deploy UI tests for Android apps. Espresso supports test creation, recording scenarios, and adding assertions, and offers fast test execution with a conducive development environment. | Custom test scenarios, Offline mode testing, Integration testing, UI testing |
| AutoFlow Studio | A modern test automation platform combining the customizability of open-source solutions with AI-powered E2E test management software. AutoFlow Studio enhances quality, streamlines operations, and uses scriptless testing with NLP capabilities. | Scriptless testing, Cross-browser testing, Cloud-based testing, Shift-left testing |
Table 2: Head-to-head comparison between popular automation tools
Regardless of these tools that can help you conduct successful automated test runs, there will always be a few challenges that you must tackle. If not addressed aggressively, these challenges can slow down your automation pipeline.
 Challenges in test automation
Challenges in test automation
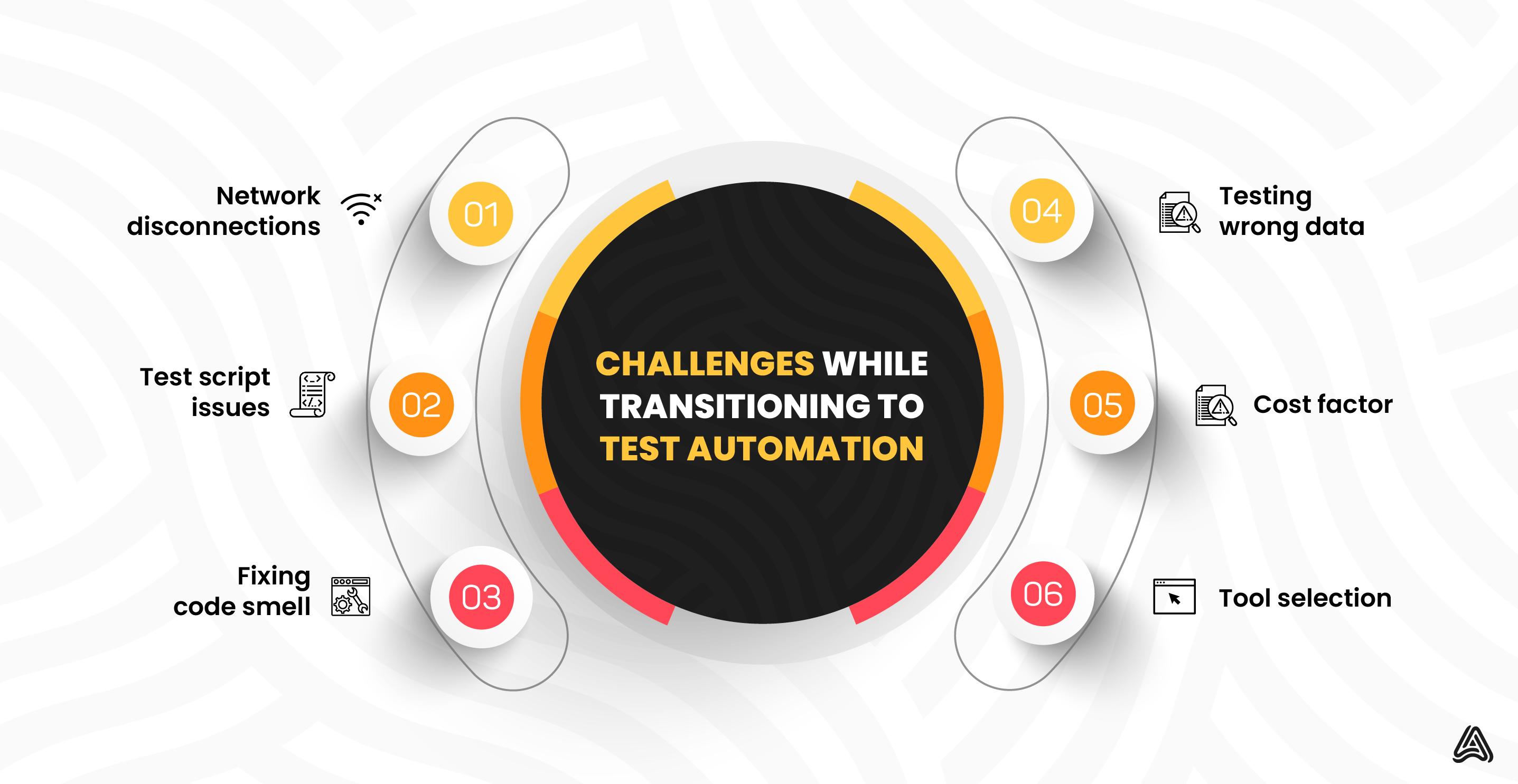
Here are a few challenges that QA teams face quite frequently and must address to avoid stumbling blocks in test automation.
 Network disconnections
Network disconnections
Erratic network connections are a significant roadblock that prevents QA teams from smoothly accessing third-party services, APIs, databases, VPNs, etc. These disconnections slow the testing process and cause unnecessary delays.
 Test script issues
Test script issues
If the QA teams lack coding skills, they may face difficulties with the test scripts. To resolve this issue, personnel can reuse test scripts to maintain their code. Treating test code as a production code can help them preserve the code efficiently. Also, periodic testing with scheduled debugging sessions and identifying critical issues with object identifiers can eliminate test script issues.
 Fixing code smell
Fixing code smell
Any attribute in the code that negatively impacts the design-build quality is a code smell. So, preserving the code quality is equally essential for programmers and testers. Automated code review tools are best suited to identify the bad smell in source codes. Fixing code smell helps QA teams accomplish the following:
- Quicker test results in less time
- Contribute to the robustness of the automation test suite
- Reduce maintenance costs and efforts effectively
 Testing wrong data
Testing wrong data
Obtaining the desirable results becomes difficult when your QA teams test against the wrong data. Relevant and accurate data are non-negotiable components for test automation to provide good results. Complicating processes and communication can also hinder testing teams from fetching the updates and most relevant data. Robust analytics and reporting solutions can help teams get faster feedback and boost productivity by minimizing data lags.
 Cost factor
Cost factor
The lack of considerable investments in the initial phases of implementing test automation prevents testers from conducting this test procedure. In addition to operational costs, management must bear licensing costs if the team isn’t using open-source tools. The right approach is to use an automation tool that helps reduce costs in all aspects of testing.
 Tool selection
Tool selection
A lack of expertise in proper tool selection can make or break the whole development cycle. The most challenging aspect is determining whether your projects need manual or automation testing. Here are a few considerations that make you select the appropriate tool.
- Compile information about your project requirements
- Gauge the technical support and assistance
- Evaluate for cross-browsing testing capabilities
- Factor in ease of maintenance
- Cost of sustenance
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Setting these challenges aside, the rise in market share for automation testing, its benefits, and upcoming features have put the demand for test suites at an all-time high. You cannot overemphasize what automation testing offers to the scope of your software development projects. With customers demanding fresh features quickly, organizations must adopt test automation to brace themselves for this task.
Keep visiting this space to discover more insightful content on the scope of test automation. Sign up for a 30-day free trial to begin your test automation journey with AutoFlow Studio.

Comments